Thoughts and opinions on all things related to IT and Network Security
Tuesday, June 30, 2009
Mozilla Foundation releases Firefox 3.5
Monday, June 29, 2009
Adobe Shockwave - New Version Addresses Security Vulnerability
All previous versions of Shockwave are affected by the vulnerability and Adobe recommend that all users update to the latest release.
Finjan Provides Free Browser Plug-In for Secure Browsing
The Finjan add-on, unlike other similar applications, actually scans the linked site for potentially dangerous content, rather than relying on details of a site's reputation. This has the potential to be both good and bad in that it does not rely on external services or databases that need to be kept up to date but it also has the potential to generate either false positives or negatives. My initial testing to date suggests that it tends to miss some of the more obvious sites that should be flagged as potentially dangerous; but I am going to continue to trial it and see what it achieves in the longer term.
If you want to give it a try Finjan SecureBrowsing can be downloaded here.
Friday, June 26, 2009
Increase in spam, phishing and malware attacks linked to the deaths of Michael Jackson and Farah Fawcett
It is worth remembering the best practice guidelines for dealing with unsolicited mail as follows:
- Do not follow web links received in unsolicited email messages
- Make sure that your anti-virus software is up to date
Security 101 - Using Wireless Hotspots - New White Paper
Firstly, let’s define what we mean by a wireless hotspot. A wireless hotspot is a wireless service in a public area such as a hotel, restaurant or coffee shop which is either provided by an external service provider or by the establishment itself. Wireless hotspots are available either as a “paid for” service or in some cases are provided free by the establishment.
Using a wireless hotspot can be risky in certain circumstances, but what are the risks and how can you mitigate them.
View the white paper here
Microsoft Release Trial Version of Free Anti-virus
In the past Microsoft has been criticised for not providing security software with Windows. It's first attempt, called Windows Live OneCar, did not attract many customers and will be discontinued. Microsoft is hoping that MSE, available as a free download, will prove more popular. Microsoft has said it will provide automatic updates.
It should be noted that MSE only provides protection against malware and does not include the more sophisticated components included in commercial rivals such as firewall, web filtering and parental controls.
Thursday, June 25, 2009
UK has cyber-attack capability
It has long been suspected that a number of nations have engaged in cyber attacks; often to gain commercial advantage for home grown companies. Lord West has said that the UK does not engage in industrial espionage but refused to be drawn of whether cyber attacks were used for military or diplomatic purposes.
Lord West stated that the UK had recruited a team of former hackers for its new Cyber Security Operations Centre, based at GCHQ.
Civil liberties campaigners are concerned as to whether these developments will lead to an extension of the government’s invasive counter-terrorism powers although the government has stated that the unit will not “be used to spy on ordinary people.”
Adobe Shockwave Player Vulnerability
Sunday, June 21, 2009
Google Launch Anti-Malvertising Service
Google's service searches a range of independent websites from other companies, service providers and security specialists dealing with the distribution of malware or advertising for specific terms, domain name etc; the more hits the more likely it is that there is something wrong. This is, however, only intended as an indication that further research is required before coming to a decision.
More information can be found at www.anti-malvertising.com.
Friday, June 19, 2009
Enabling Encryption on Gmail
1. Log into your Gmail account in the normal way and click on "Settings" at the top of the screen; this will display Gmail's settings.
2. Select the "General" tab (if it is not already selected) and scroll to the bottom of the screen. You are looking the "Browser Connection" options show in the picture below (click on the picture to see a larger version).
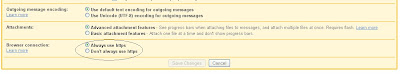
3. Select "Always use HTTPS" and then click "Save Changes". Your Gmail account will now use HTTPS for all communications, reducing the possibilities for "man in the middle" type attacks.
Our recommendation is always to use HTTPS although this is particularly important if you are planning on using insecure Internet connections such a public Wi-Fi or Internet cafes.
Google Tackled Over Gmail Security
A key concern of the signatories is that, as more of us used insecure Internet access – such as public wireless networks – there is a risk of sessions being hijacked by criminals who could then impersonate the genuine user.
Google currently only protects the log in process as user’s sign in, as soon as the sign in process has completed encryption is turned off. It is possible to force Gmail, Google Docs and Calendar into using encryption all the time but the option is difficult to find and many users simply retain the default settings. Every web mail provider currently faces the same problem.
Parcelforce Leak Personal Data
Customer using Parcelforce Worldwide to send packages are given a reference number, which allows them to track the progress of their delivery but when this reference number was entered the ParcelForce tracking system displayed details of unrelated deliveries, including some parcels that had already been delivered.
ParcelForce have corrected the problem, which occurred after upgrade work on Wednesday night and have apologized to customers.
Security 101 - Understanding Firewalls
Firewalls come in two forms: hardware and software. Hardware firewalls are external devices that are normally positioned between your computer or network and your Internet connection. In the case of home users, your Internet Service Provider may have provided a device described as a “router” that incorporates some firewall functionality.
Hardware Based Firewalls
Hardware based firewalls are particularly good for protecting multiple computers but also offer a high degree of protection for a single computer. If you only have a single computer behind the firewall or you can be certain that all of the other computers on the network are up to date on patches and a free from malicious software you may not need the additional protection that can be provided by installing a software based firewall.
Hardware firewalls have the advantage of being separate devices running their own operating systems and as such provide an additional line of defence against attacks. The main drawback of hardware based firewalls is cost.
Software Based Firewalls
Some operating systems provide built in firewall functionality; if the operating system that you are using includes this functionality you should consider enabling it. If your operating system does not provide this functionality there are a number of free, shareware and commercial offerings available. We recommend that firewall (and other security software) is only ever installed from a CD/DVD obtained from a trusted source as this mitigates the risks associated with installing software downloaded from the Internet. If you do want to install security software from the Internet make sure it is from a reputable, secure web site.
Although, it is possible to rely on a software based firewall alone, this is not recommended as having the firewall on the same computer that you are trying to protect limits the firewall’s ability to catch malicious traffic before it enters your system.
What is the best approach?
The best possible approach is to utilize a hardware firewall between your network and the Internet and install (or enable) software based firewalls on all the computers on your network as this will mitigate the effects of attack by external parties and also provide a level of protection against viruses, worms or other malicious software spreading throughout your own network.
Configuration Options
Most commercial firewall products will have a configuration that is acceptable secure for most users but, since each firewall is different, you’ll need to read and understand the documentation that is provided with the firewall to understand whether its default settings are sufficient for your needs.
Be Vigilant
The key thing to remember is not to be lulled into a false sense of security. While firewalls can limit the possibilities for external attacks and software-based firewalls can provide a degree of protection against malicious software spreading throughout your network, firewall provide little or no protection against malicious software that spreads by email (by tricking you into to clicking on attachments) or compromises web sites. Even if you have firewalls installed you should still make sure that your anti-virus software is up to date and that you exercise caution in the websites that you visit.
Thursday, June 18, 2009
Windows 7 Security Hole Still Open
The purpose of UAC is to guard against malware - it warns the user when applications try to make changes to the computer but "proof of concept" code has been created that can remotely disable UAC without informing the user that this happened. Microsoft have so far started that this is a feature that has been included by design and, therefore, will not be fixed.
Microsoft Optical Desktop 1000 and 2000 keyboard vulnerabilities
Currently only Microsoft's wireless keyboards transmitting on the 27 Mhz band are vulnerable; Bluetooth keyboards are not at risk.
The vulnerabilities in Microsoft keyoboards have been known about since December 2007 but as yet there are no indications that Microsoft has taken steps to mitigate the them.
If you want to use a wireless keyboard the answer, for now at least is to use a Bluetooth device otherwise use a wired keyboard.
Your Computer Might be Traded Online - Without Your Knowledge
Golden Cash also provides an exploit tool kit for infecting PCs and manipulating websites. Finjan's report suggests that this platform represents a highly lucrative system. See Finjan's report here for more details.
New web server attack
The HTTP protocol allows clients to split the data from a GET or POST request over a number of HTTP queries; depending on the server configuration, the first such request can cause the server to allocate a large amount of resources for the response while waiting for the rest of the request. The web servers that are vulerable to this type of attack are those that implement strategies to avoid system overloads by, for example, limiting the number of simulataneous HTTP queries. These include Apache HTTP server, DHTTPD, GoAhead Web Server and Squid, but not Microsoft IIS or Light HTTPd. The basic concept behind this new attack is similar to the half-open TCP connections attacks that have been seen in the past, except that this attack generally only affects the HTTP component of the server and other services are largely unaffected.
There are a number of ways to defend against this attack; web servers could be protected using load balancers and web application firewalls that only forward complete HTTP requests to the server or the reducing the time out for HTTP requests.
Apple release iPhone OS 3.0
Wednesday, June 17, 2009
Six Ways to Protect Your Wireless Network
Most wireless LAN hardware is incredibly easy to set up and, in the case of hardware supplied by broadband providers, is often supplied pre-configured. However, it is worth checking the security configuration of your wireless LAN router; here are some simple things you can do to protect your wireless network.
Secure the administration interface. Wireless routers generally have an administrator password that must be entered before the configuration can be changed. Most devices will be preconfigured with a default administrator password and some devices will have no password at all. You should always ensure that an administration password is configured or, if the device has a default password, change it. If you leave the device with no password or with the password set to a default value you run the risk of the device being reconfigured without your knowledge; either by somebody who has managed to attach to your network or by malware that you have inadvertently downloaded.
Use WPA encryption instead of WEP. 802.11’s WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) encryption has weaknesses that make is relatively easy to crack the encryption and access the wireless network. A better encryption standard is WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access) which provides much better protection and is easier to use. WPA support is built into almost all modern wireless hardware and operating systems. WPA2 is a more recent version of the standard which provides even stronger encryption.
It is possible that you may have some devices that do not support WPA (often devices such as media players, PDAs etc). In this situation it is tempted to turn encryption off completely but this really will leave you wide open to attack. WEP encryption, for all its flaws, is better than nothing and therefore should be used where you have devices that do not support WPA. If you do use WEP make sure that you do not use an easy to guess encryption key. You should also consider changing the WEP encryption key at least once a week.
Don’t broadcast the SSID. Most wireless access points and wireless routers continuously broadcast the wireless network’s name, this is also called the Service Set Identifier or SSID. The purpose of this is to make it easy to configure wireless networks as wireless devices will be able to identify the wireless networks that are available. However, it also advertises the presence of your wireless network to any wireless systems in range. Turning of SSID broadcast will make your wireless network invisible to your neighbours and the casual intruder but it will still be visible to anybody with a wireless network sniffer.
Use MAC filtering. The MAC address is a hardware address associated with a network adaptor and, unlike and IP address, is globally unique to that adaptor. By using MAC filtering on your wireless access point or router you can control the specific devices that are permitted to connect to it. MAC addresses can be spoofed by somebody with sufficient knowledge, so this does not provide an absolute guarantee of security but it does give the attacker another hurdle to jump.
Disable remote administration. Many wireless LAN routers can be administered remotely from the Internet. You should only every use this feature if you are also able to define a specific IP addresses or a limited range of IP addresses that are able to administer the router. If you are not able to do this anyone, anywhere could potentially access your router. Unless you particularly need this feature it is best to disable it; most wireless LAN routers disable this feature by default but it is always worth checking.
Reduce the Wireless LAN transmitter power. This feature does not exist on all wireless LAN routers and access points, but some will allow you to decrease the power of the transmitter thereby reducing the range of the signal. It is usually impossible to fine-tune the signal to the point where it does not leak outside your premises but you can limit how far the signal reaches thus reducing the opportunity for people outside your premesis to access your wireless LAN.
Eye Chart Test for Conficker
Conficker (also known as Downadup, Kido) blocks access to over 100 anti-virus and security websites. If you are blocked from loading the remote images the first row of the table (popular anti-virus and security web sites) but not blocked from loading the remote images in the second row (alternative operating systems) it is an indication that your computer may be affected by Conficker of some other malware.
The Conficker Eye Chart can be accessed here.
Tuesday, June 16, 2009
Apple Releases Java Updates for Mac OS X 10.4 and 10.5
Monday, June 15, 2009
New malware for Mac OS X
Security experts have discovered two new forms of MacOS X malware both of which were foiund on popular pornographic websites. Historically, the MacOS platform has had very little in the way of virus and trojans; but attacks against the Mac platform have been increasing.
The small amount of malware in circulation for the Mac platform has made some Mac owners complacent; Mac owners are less likely to running antivirus software, for example. This complacency has not been helped by Apple's approach to marketing.
Sunday, June 14, 2009
Scareware, beware!
In its latest update, Microsoft has added code that detects and deletes the widespread Internet Antivirus Pro family of fake security programs. These programs, often referred to as scareware, are becoming more and more popular with high tech criminals. It is estimated that there were more than 9,000 bogus anti-malware programs in circulation in December 2008.
Recently the US government has moved to shut down some of the companies that have been peddling programs that falsely claim to find malcious software on PCs and then charge for the non-existant threats to be removed. As well as claiming to remove non-existant threats, the Internet Antivirus Pro software contains a password stealer that grabs login details.Microsoft set to give away anti-virus software
Thursday, June 11, 2009
The nice things about standards ....
ISO/IEC 27001:2005
The ISO/IEC 27001:2005 standard covers all types of organisations and specifies the requirements for implementing, operating, monitoring, reviewing, maintaining and improving a documented Information Security Management System (ISMS) and relates this to the organisation's overall business risks.
ISO/IEC 20000:2005
This standard was developed to reflect the best practice guidance contained within the Information Technology Infrastructure Library (ITIL) framework. It consists of two part: Specification for IT Service Management and code of practice for service management. ITIL enables organisations to define a model to manage their IT operations covering areas such as service delivery, relationship management, resolution process, control processes, release processes, changed services and service management.
ISO/IEC 18028:2006
This was developed to define a standard security architecture that describes a framework to support the planning, design and implementation of network security. This standard had major contributions from the ITU X.805 standard.
PCI DSS 1.1:2006
The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI-DSS) includes requirements for security management, policies, procedures, network architecture, software design and other critical measures. It is desgined to help reduce the frequency and impact of security incidents in the processing of payment cards. PCI-DSS is appliable to any oragnisation that is processing card payments.
This is a brief review of four major security standards and their relevance to different types of organisation.